Overview
The following figure will give you a quick overview on the architecture of DIVA. In the following chapter we will take a close look at main components and explain their responsibilities. Following the navigation structure in the left sidebar you will consistently learn the architecture and be able to understand the implications and design decisions.
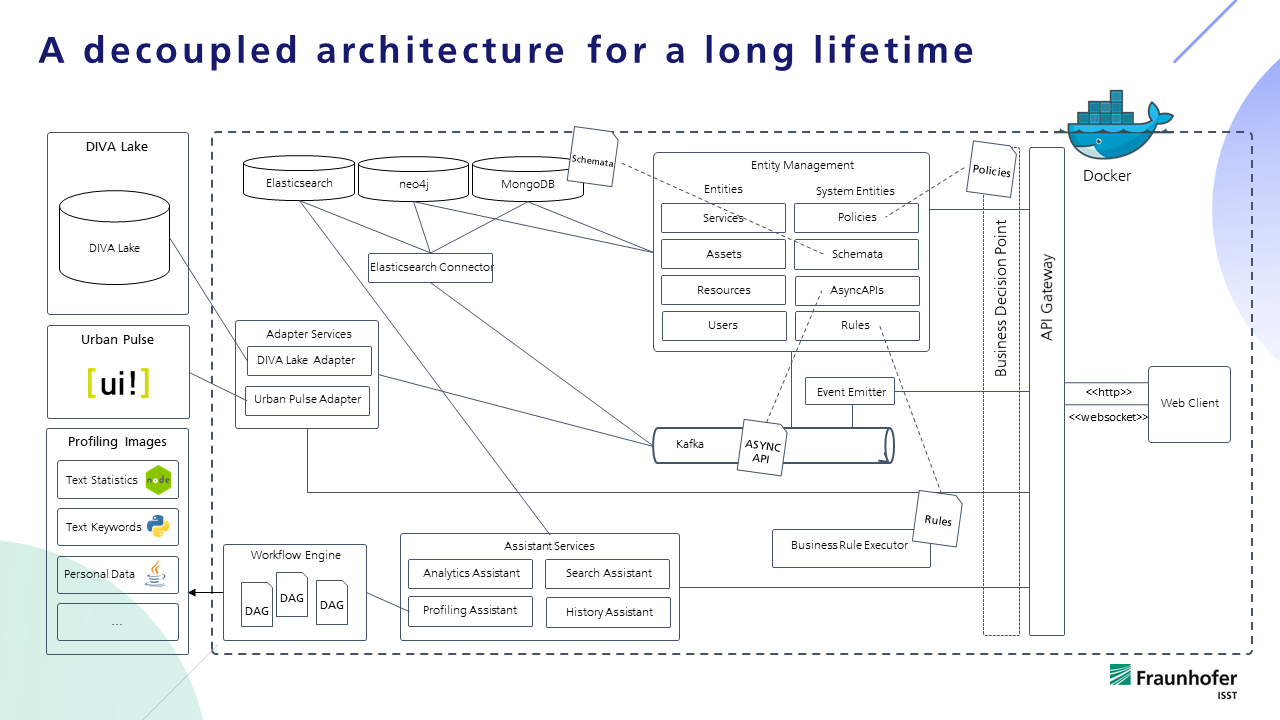
The DIVA architecture follows the microservice pattern and aims at high degree of scalability. The main goal is to provide the most simplistic components and strong modularity for scalable extension of the system with new functionalities.
We have five types of services, which are distinguished from each other by well-defined competences. At one hand, we have management services. Management Services are derived from our data model and perform the operations on the corresponding entities. On the other hand, there are Assistant Services, which are responsible for additional useful functions. To be able to connect DIVA with external sources like UrbanPulse or DSC, we develop the third service type - Adapter Services. Connector Services are used to internally replicate metadata from primary MongoDB data store to other data stores.
All services provide an API which is strictly defined using OpenAPI specification. The web client uses API Gateway to access the backend, API Gateway acts as an abstraction layer for the underlying services. Kafka messages allow services to communicate indirectly and asynchronously with each other.
In the following the components will be explained with more details.
Data Model
Our data model aims at simplicity and flat hierarchy. We have designed a model with loose entity coupling, driven by JSON schemas. JSON schemas are most important building block of our whole system. Thanks to the schema-driven development process, we can achieve high integrity and validity of the data processed in DIVA. Furthermore, this approach allows us to develop Management Services API's with fully automated data validation process.
An entity is a logical high level abstraction that represents common properties of the underlying entities and does not exists physically.
The entities User, Resource, Asset etc. inherit properties like id, entityType and created from Entity.
You will find schematas for all entities in core/services/entity-management/defaultEntities/jsonSchemata/ directory.
Although the entities are not coupled with each other, they can have relations. All entities are created by an actor (User or Service). An Asset can group multiple Resources, Asset and Resources can have multiple Reviews and History entries. The relation is expressed in neo4j by edges. So if one entity is in relation to another, you can set and resolve this in the neo4j database.
In this way we can achieve a flat hierarchy, loose coupling and flexible relations between entities. This in turn allows us to develop services with transparent API according to the single responsibility principle. You will learn more about our REST API design rules in the corresponding section.
Relations
Note that even if the entities have relations, they remain (mostly) fully independent and can be managed on their own. The existence of one entity is not bound to another one. Sometimes you want this behavior. it can be achieved by writing a business rule that e.g. deletes reviews of an deleted entity.
DCAT Compatibility
DCAT 3
In this case, compatible means that a parser (that currently does not exist) can transform our internal metadata model into DCAT 3. It may be that DCAT allows a higher cardinality than the metadata model in DIVA. Nevertheless, DIVA would be compatible at this point. The reverse case may also occur. However, then we would not have compatibility.
caution
Currently we do not have a complete overview of which fields are DCAT compatible. This is still to be done.
DIVA Core
Under the DIVA Core we understand all components that are implemented and packaged by us or are necessary for the basic functionality. This includes, for example, management services that we have written or external open source products such as MongoDB or Kafka, which are fixed parts of the DIVA ecosystem.
Web Client
Web application is currently the only client that allows managing DIVA Catalog through a nice UI. For non-developers this is the only way to interact with the system's backend. Make sure to take a look at the users guide!
API Gateway
The Kong API Gateway acts as a secure access point to the backend services. It is an abstraction layer for the REST APIs of the individual services used by our Web client. Only authenticated users with a valid JWT have access to the backend through the API Gateway.
Messaging
We use Kafka as the event bus for the asynchronous communications between the components. The messages structure is regulated through the AsyncAPI schema. The management Service produces events indicating data changes on corresponding topics. To guaranty consistency and integrity of the exchanged data, the services validate the messages against AsyncAPI schema while consuming and producing them.
Data Storage
DIVA uses four databases as persistent data store, including MongoDB, neo4j, Elasticsearch and MinIO. MongoDB and neo4j are the primary metadata storage for all kind of DIVA entities (users, resources, assets etc.), their relations and is always the source of truth. MongoDB and neo4j should be used to reach consistency across other external or internal components.
Relevant entities metadata is replicated to the Elasticsearch instance through the Elasticsearch Connector to provide high performance full text search capabilities. This ES instance is used by the Search Assistant Service. MinIO acts as the efficient object storage, where we only persist files imported via Web client UI from the user's device.
Data Replication
Data replication across different external or internal components should be achieved through events messaging. Please note that this can lead to eventual consistency due to the asynchronous nature of events broadcasting. MongoDB and neo4j in combination always act as the single source of truth!
Entity Management
Management Service exposes API for CRUD operations on the entities that are available.
It is an important part of the system that represent the main concept of the data modeling in DIVA.
All changes applied to the data produce Kafka events so other components can react properly to these changes.
The entity data is stored in the entities collection in MongoDB and as nodes in the neo4j database.
| Entity Name | Entity Type |
|---|---|
| Resource | resource |
| Asset | asset |
| Service | service |
| User | user |
| JSON Schema | systemEntity |
| Async API | systemEntity |
| Policies | systemEntity |
| Business Rules | systemEntity |
Assistant Services
Assistant Services provide useful functionalities to extend DIVA possibilities. They do not produce or mutate any data and have only read access to the entities.
| Title | Description | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|
| Analytics Assistant | provides statistical data about catalog entities | Elasticsearch |
| Profiling Assistant | Responsible for profiling workflows execution triggering | MongoDB, Airflow |
| History Assistant | Provides a human readable representation of the entities history | MongoDB, Schema Registry |
| Search Assistant | Provides preselected entities search API | Elasticsearch |
Adapter Services
The Adapter Services are special services designed to connect and import data from external sources. They encapsulate the connection logic, load the data, transform it into a DIVA compliant representation and store the newly created Resources in the system. In special cases an Adapter Service can be implemented to export a DIVA Resource to an external system. The creation of new resources is done by using the Resource Management Service, direct access to the data storage is only allowed in the read mode.
| Title | Description | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|
| DIVA Lake Adapter | Responsible for uploading files into our Diva Lake (MinIO) | MinIO, Resource Management |
| UrbanPulse Adapter | Adapter for the UrbanPulse instance | UrbanPulse, Resource Management |
Workflow Engine
Apache Airflow is a great open-source workflow tool tha we use to execute and orchestrate profiling tasks. Profiling Assistant is our wrapper service for Airflow API that triggers the workflow execution.
Functions as a Service (FaaS)
In DIVA, there are a number of useful analysis tasks that are performed frequently. We build small Functions-as-a-Service that simply produce an output for a given input to address such specific profiling tasks. These functions are stateless and are a part of the profiling workflow engine.